British Windward Islands
British Windward Islands | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1833–1958 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Motto: I pede fausto (Latin: Go with a lucky foot) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Anthem: "God Save the King" | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Status | British colony | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Capital | Bridgetown, Barbados (1871–1885) St George's, Grenada (1885–1958) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common languages | English English-based creole languages Dominican Creole French Saint Lucian Creole French | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Religion | Christianity (Anglican, Catholic, Methodist) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Government | Constitutional monarchy | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monarch | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
• 1833-1837 (first) | William IV | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
• 1952–1958 (last) | Elizabeth II | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Governor-in-chief | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
• 1833–1836 (first) | Lionel Smith | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
• 1955–1960[a] (last) | Colville Deverell | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
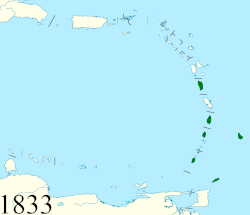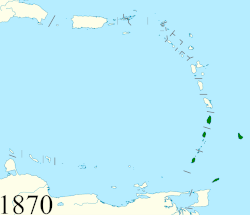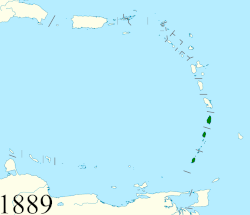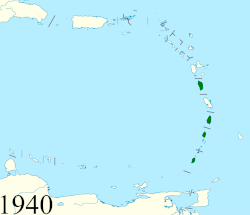
• Established | 1833 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
• Federation | 1871 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
• Barbados left | 1885 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
• Tobago left | 1889 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
• Dominica joined | 1940 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1956 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 January 1958 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Currency | Pound sterling (official) Spanish dollar, Mexican peso also used | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
The British Windward Islands was an administrative grouping of British colonies in the Windward Islands of the West Indies, existing from 1833 until 3 January 1958 and consisting of the islands of Grenada, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent, the Grenadines, Barbados (the seat of the governor until 1885, when it returned to its former status of a completely separate colony), Tobago (until 1889, when it was joined to Trinidad), and (from 1940) Dominica, previously included in the British Leeward Islands.
Administrative history
[edit]The seat of government was Bridgetown on Barbados, from 1871 to 1885, and thereafter St. George's on Grenada. The islands were not a single colony, but a confederation of separate colonies with a common governor-in-chief, while each island retained its own institutions. The Windward Islands had neither legislature, laws, revenue nor tariff in common. However, there was a common audit system, while the islands united in maintaining certain institutions of general utility.
Judicial history
[edit]In 1859 a common court of appeal for the group was established, composed of the chief justices of the respective island colonies. Under the West Indian Court of Appeal Act 1919 this court was replaced by the West Indian Court of Appeal, responsible for appeals from not only the Windward Islands but also the Federal Colony of the Leeward Islands, Barbados, Trinidad and Tobago, and British Guiana.
In 1939 the Windward and Leeward Islands Supreme Court and the Windward and Leeward Islands Court of Appeal were established, which was replaced in 1967 by the Eastern Caribbean Supreme Court which provides both functions.[1]
- Chief justices of the Windward and Leeward Islands
- 1940–1942 James Henry Jarrett[2]
- 1943–1950 Sir Clement Malone[3]
- 1950–1957 Sir Donald Jackson[4]
- 1958–1963 Sir Cyril George Xavier Henriques[5][6][7]
- 1963–?1967 Frank E. Field[8]
See also
[edit]- List of governors of the Windward Islands
- History of the British West Indies
- Windward Islands
- British Leeward Islands
- Windward Islands cricket team
Notes
[edit]- ^ The office of governor-in-chief was officially abolished on 1 January 1960, although the territory had been abolished two years earlier.
References
[edit]- ^ Lawrence Albert Joseph. "The Origin of the Supreme Court of Grenada". The Barnacle. Granada: The Barnacle News. Archived from the original on 20 November 2015.
- ^ "Named Chief Justice. London, Feb. 5". The Ottawa Journal. Ottawa, Canada. 6 February 1940. p. 3 – via Newspapers.com.
The Colonial Office tonight announced appointment of J. H. Jarrett, now Colonial Secretary of the Bahamas, as chief justice of the Windward and Leeward islands.
- ^ "No. 36056". The London Gazette. 15 June 1943. p. 2739.
- ^ "No. 39904". The London Gazette. 3 July 1953. p. 3677.
- ^ Chief Secretary's Office (5 February 1959). "Ref. No. P.F. 770". The Antigua, Montserrat and Virgin Islands Gazette. Vol. 4, no. 8. by Authority. p. 1.
Mr. Henrique's appointment became effective on 24th December, 1958.
- ^ "No. 41534". The London Gazette. 28 October 1958. p. 6590.
The Queen has been pleased to give directions for the appointment of Cyril George Xavier Henriques, Esq., (Commissioner for Law Revision, British Honduras) to be Chief Justice of the Supreme Court, Windward and Leeward Islands.
- ^ "No. 42870". The London Gazette (Supplement). 1 January 1963. p. 2.
- ^ Government House (23 January 1964). "Appointment of Chief Justice of the Windward and Leeward Islands". The Antigua, Montserrat and Virgin Islands Gazette. Vol. 9, no. 5. by Authority. p. 21.
The Secretary of State for the Colonies ... has appointed Mr. Justice Frank E. Field to the office of Chief Justice of the Windward and Leeward Islands with effect from 2nd December, 1963.
Sources
[edit]- This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Windward Islands". Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 28 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 716.
External links
[edit]- Queen and Commonwealth: Other Caribbean realms for the official website of the British monarchy
- U.S Library of Congress – Barbados and the Windward Islands colony
- WorldStatesmen.org
- British Windward Islands
- British West Indies
- Windward Islands
- Former British colonies and protectorates in the Americas
- Former countries in the Caribbean
- Former colonies in North America
- Former federations
- History of British Grenada
- History of the Colony of Barbados
- History of British Dominica
- History of British Saint Lucia
- History of British Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
- History of Tobago
- States and territories established in 1833
- States and territories disestablished in 1958
- 1830s establishments in the Caribbean
- 1833 establishments in the British Empire
- 1958 disestablishments in the British Empire
- 1833 establishments in North America
- 1958 disestablishments in North America


